Behavioral Neuroscience
Summers
Sensory input for Rhythmicity
Afferent path to the SCN
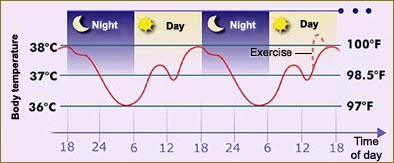
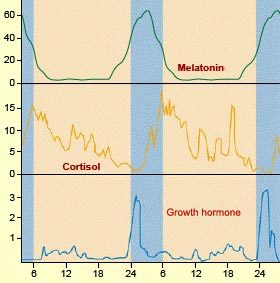
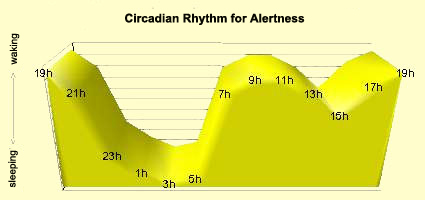
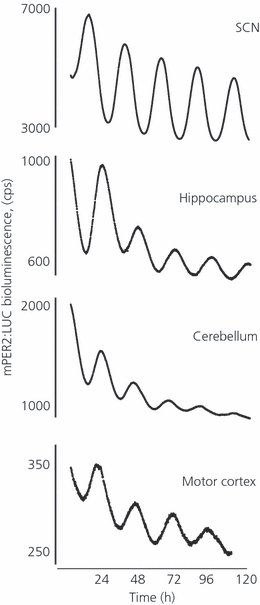
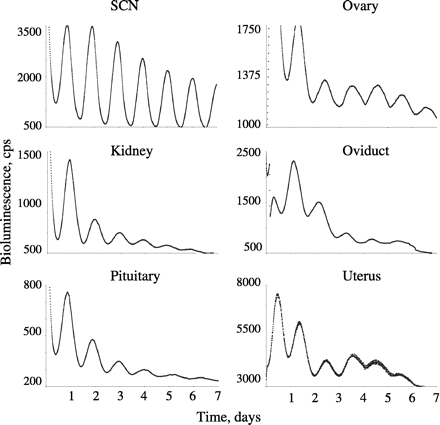
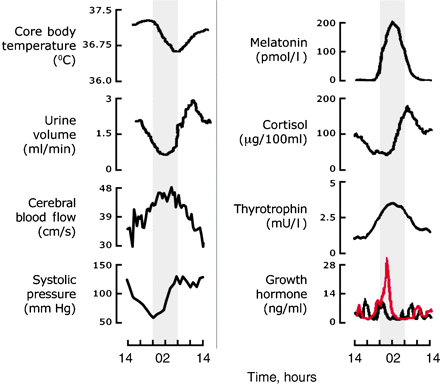
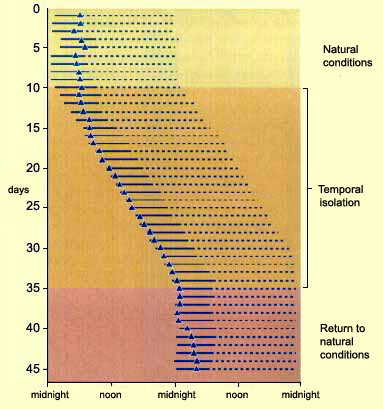
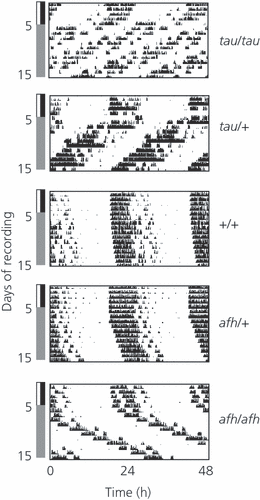
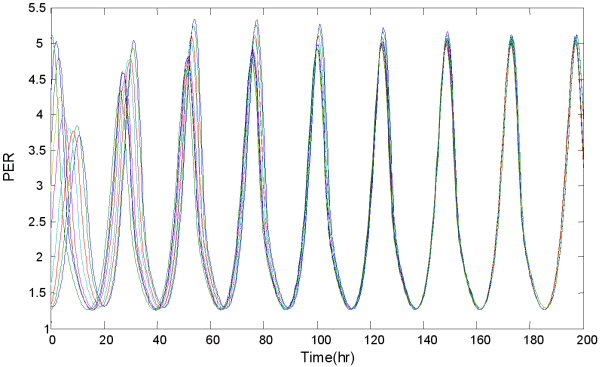
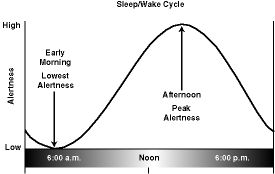
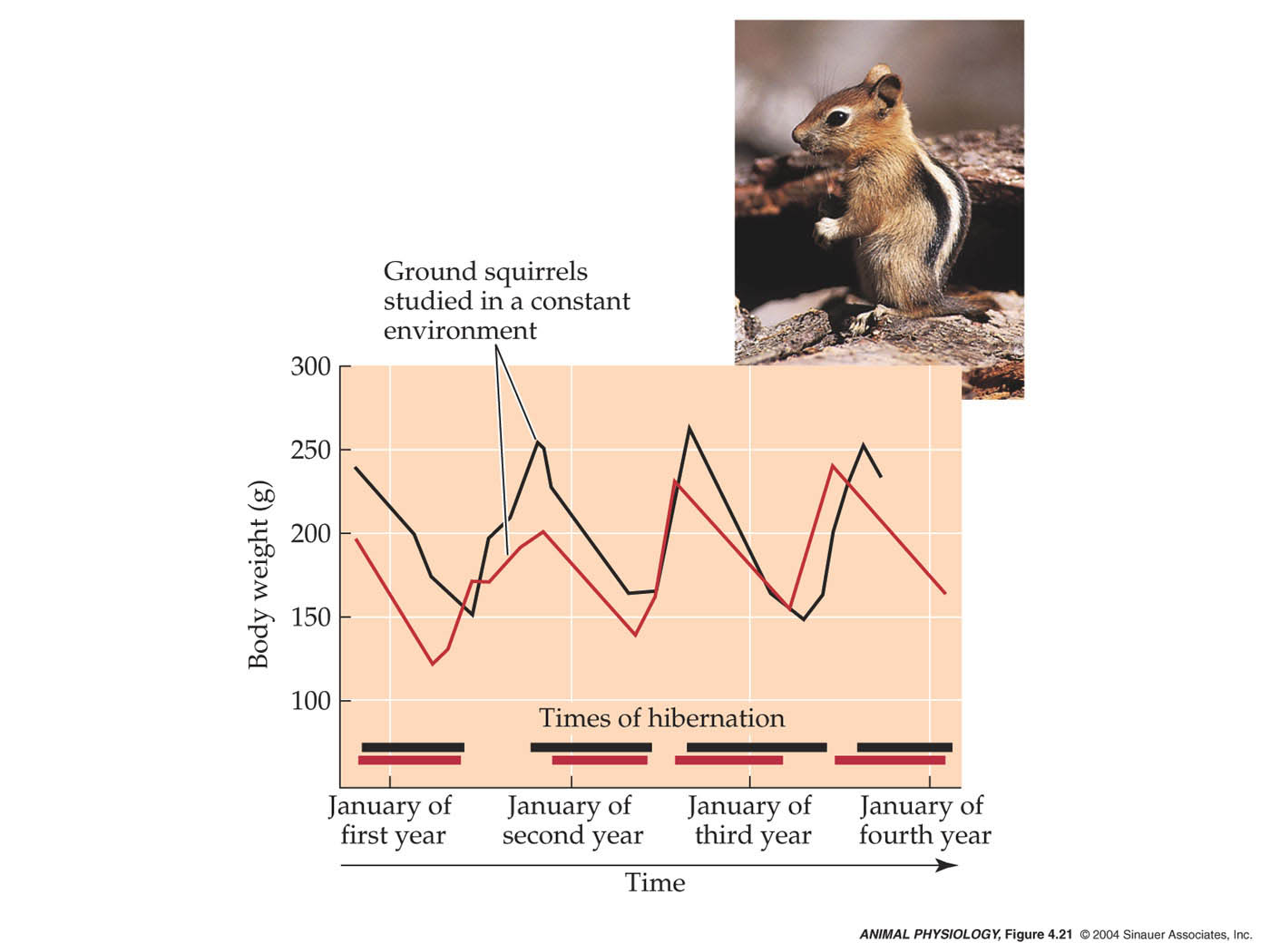
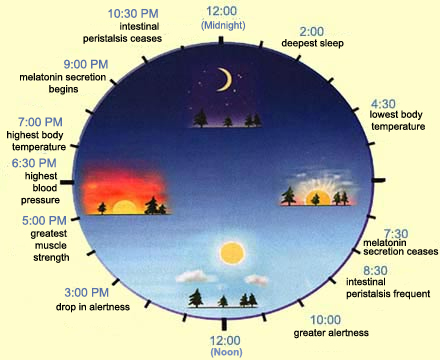
Figures of Rhythmicity
Retina-RGC-SCN
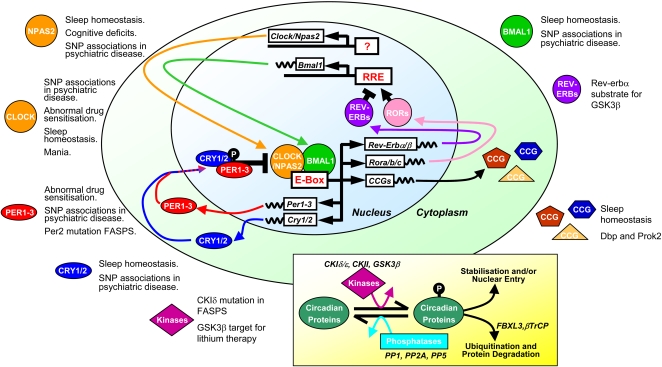
Efferent SCN output
Integration of Rhythms into Behavior
Molecular SCN
end Acronyms/Abbreviations Syllabus
VIP
AVP
GABA
5-HT
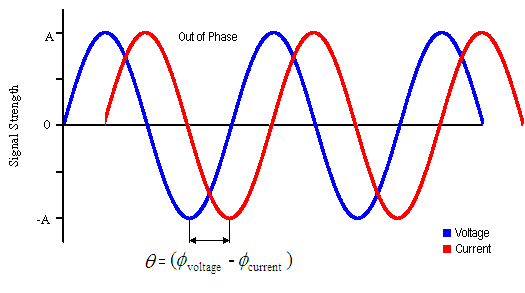
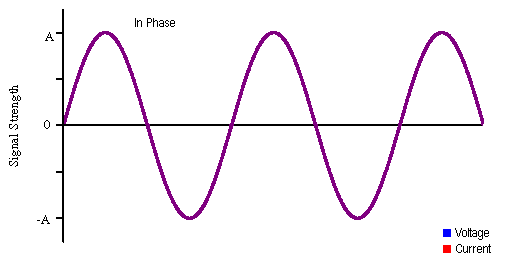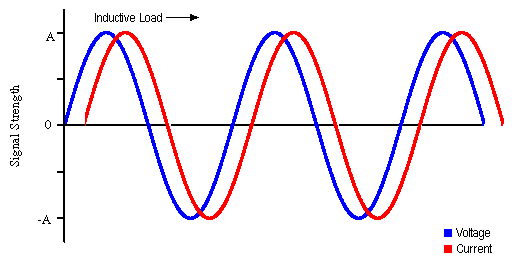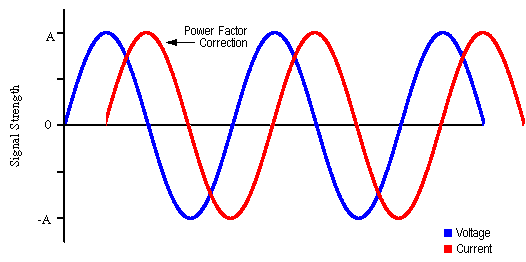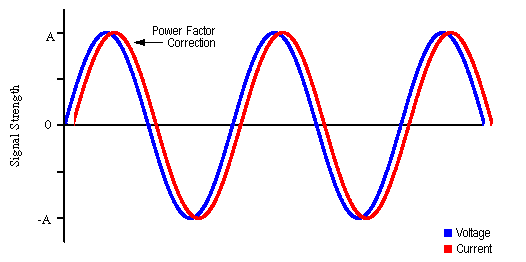
 the Brain from Top to Bottom
the Brain from Top to Bottom